Introduction
Inherent Safety in Plant Design is a new concept in the modern world in the overall Plant Safety spectrum. This Concept is very much prevalent in US and Europe but its explicit applications in Indian plants are not visible(perhaps due to overdependence of the Refineries and Oil/gas Plants on Engineering Contractors keen on selling out of shelf Designs). This concept bestows safety, cost optimization and productivity improvement to the projects and operating companies. This can be applied during Plant’s FEED Stage, Detailed Design, Operation and Commissioning and Shutdown stages.
Inherent Safety in Design
This is an approach to prevent chemical accidents, that it differs fundamentally from secondary accident prevention and mitigation approaches. Inherent safety (primary prevention) develops technologies and strategies which prevent or reduce the initiation frequencies of a chemical accidents. Whereas, Layers of Protection (secondary prevention or mitigation approaches) reduce the probability of a chemical accident; mitigation and emergency responses reduce the seriousness of injuries, property and environmental damage.
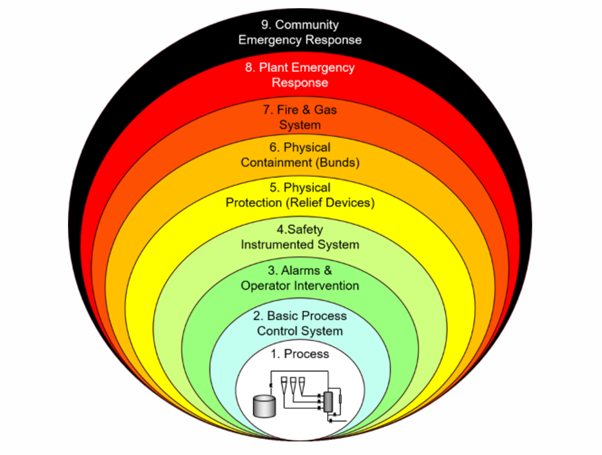
As shown in the diagram above, ISD mainly targets item 1. Process and item 2.Basic Process Control system. Inherent Safety in Design eliminates the process hazards and therefore moderates the need for expensive layers of protection (items 3 through 7 in the diagram above). However, some Basic Process Control Systems (BPCS) and Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) play an important role in improving the safety and reducing the risk.
ISD Domains
Following are the domains for ISD:
- Design,
- Fabrication and installation,
- Operating strategy,
- Environmental Factors,
- Human Factors and
- Safety Management System.
ISD Strategies
Following ISD strategies are applied in above domains:
- Minimize safety hazard,
- Substitute safety hazard,
- Moderate safety hazard,
- Simplify the system,
- Limit Error Tolerance
- And document and implement Limit Effects.
Domains application of ISD in a Plant:
Category | ISD application |
1. Feed Design | 1.1Analyze hazard potential of Feeds, products, catalysts, byproducts with respect to their Reactivity, Toxicity, flammability, Combustibility Heat of Reaction. Based on this data explore to minimize the inventory of high potential hazard substances and substitute them with lesser hazard potential substances. |
| 1.2 Develop a PFD based on Aspentech or some other software. Determine the Operating envelope. |
| 1.3 Carry out a preliminary sizing of major equipment and calculate inventory of all hazardous substances. |
| 1.4 Develop a plant layout and place all the equipment as per item 1.2 and item 1.3 as well as process utilities. |
| 1.5 Analyze selected process scheme with a plant lay out as per item 1.4 through PHA followed by a quantitative hazard analysis. If the selected process scheme quantitatively meets the consequence effect targets, select this process scheme, otherwise go for a substitute scheme. |
2.Detailed Design | 2.1 Apply most stringent design Standards |
| 2.2 Adequate and comprehensive definition of design basis |
| 2.3 Stringent Material Specification |
| 2.4 Application of Management of Change during design changes |
| 2.5 Consequence modeling based process plant, process unit and equipment siting and modifying the plant lay out accordingly. |
3.Fabrication and Installation | 3.1 Institution and Enforcement of Quality System |
| 3.2 Correct Material of Construction |
4.Operating Strategy | 4.1 Do not operate close to operating envelope limits |
| 4.2 Avoid a design with frequent thermal cycling of high temperature equipment |
| 4.3 Design for Reactivity embrittlement as applicable |
5.Environmental Factors | 5.1Internal/External Corrosion Management |
| 5.2 Vibrations Management |
6.Human Factors | 6.1Skill Based, Rule Based and Knowledge Based Errors avoidance |
| 6.2 Abnormal Situation Awareness and its handling |
| 6.3 Alarm Philosophy and Management |
7.Safety Management | 7.1Process Safety Management |
| 7.2 Management of Change |
8. Facility siting | Units, equipment siting on Hazard consequence analysis basis |
9.Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis(HIRA) during Technology selection | Ø Minimize hazard, Ø Substitute hazard, Ø Moderate hazard, Ø Simplify the system
|
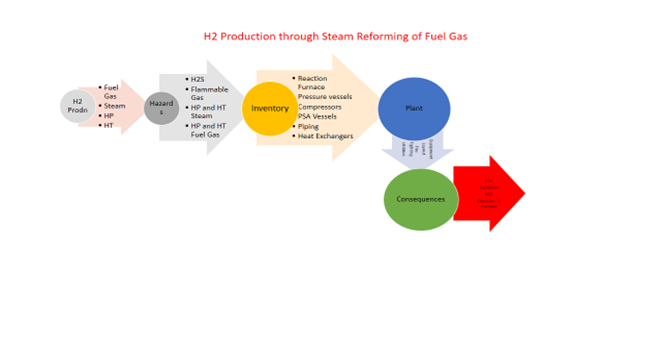
ISD Example of H2 Production through Steam Reforming Vs Water Electrolysis